-
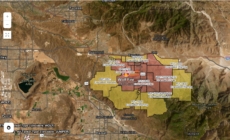
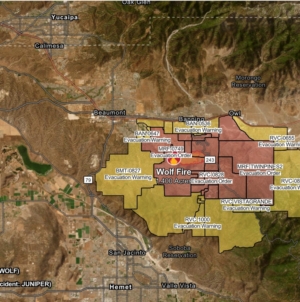
California Fire Evacuation Map Shows Where People Told to ‘Leave Now’ - 21 mins ago
-
Cancer Curtailed British Royal Family’s Public Engagements - 25 mins ago
-
Royal Tradition Ends After 156 Years—King Charles Ditches Royal Train for Helicopters - 55 mins ago
-
Gaza City Cafe Hit by Deadly Strike - about 1 hour ago
-
Lakers, LeBron James Rumors Receive Huge Update - 2 hours ago
-
Teen Mt. Whitney hiker who walked off 120-foot cliff in delirium makes slow recovery, family says - 2 hours ago
-
Dangerous Heat Grips Much of Europe, With More to Come - 2 hours ago
-
North Korea Ignores Trump’s Overtures - 2 hours ago
-
Trump Vowed to Dismantle MS-13. His Deal With Bukele Threatens That Effort. - 3 hours ago
-
WWE Legend Ric Flair Set To Undergo Surgery - 3 hours ago
For Patients Needing Transplants, Hope Arrives on Tiny Hooves
More than 100,000 Americans are on waiting lists for donor organs, most needing a kidney. Only 25,000 human donor kidneys become available each year. Twelve Americans on the kidney list die every day on average.
Scientists first transplanted genetically engineered pig organs into other animals and then to brain-dead human patients. In 2022, researchers received permission to transplant the organs into a few critically ill patients, and then, last year, into healthier people.
Now, for the first time, a formal clinical study of the procedure is being initiated.
“Just imagine, you have kidney disease and know your kidneys are going to fail, and you have a pig’s kidney waiting for you — and you never see dialysis,” said Mike Curtis, president and chief executive at eGenesis.
He foresees a future in which genetic engineering will make pig organs so compatible with humans that patients won’t have to take powerful drugs that prevent rejection but make them vulnerable to infections and cancer.
Babies born with serious heart defects might be given a pig’s heart temporarily while waiting for a human donor heart. A pig’s liver could potentially serve as a bridge for those in need of a human liver.
Some scientists argue that there is a moral imperative to move forward.
“Is it ethical to let thousands of people die each year on a waiting list when we have something that could possibly save their lives?” asked Dr. David K.C. Cooper, who studies xenotransplantation at Harvard and is a consultant to eGenesis.
“I think it’s beginning to be ethically unacceptable to let people die when there’s an alternative therapy that looks pretty encouraging.”
But critics say xenotransplantation is a hubristic, pie-in-the-sky endeavor aiming to solve an organ shortage with technology when there’s a simpler solution: expanding the supply of human organs by encouraging more donation.
And xenotransplantation is freighted with unanswered questions.
Pigs can carry pathogens that can find their way to humans. If a deadly virus, for example, were to emerge in transplant patients, it could spread with catastrophic consequences.
It might be years or even decades before symptoms were observed, warned Christopher Bobier, a bioethicist from the Central Michigan University College of Medicine.
“A potential zoonotic transference could happen at any point after a transplant — in perpetuity,” he said. The risk is believed to be small, he added, “but it is not zero.”
Source link